Dentistry for Children
Teething
 For most parents, the sudden appearance of the child's first tooth is a momentous occasion. Physicians have also attached great significance to the emergence of primary (milk) tooth/teeth. When the first tooth cuts the gums and starts to erupt, a local inflammatory process occurs which is associated with redness, tenderness, swelling, fever etc. As this process continues, the child puts whatever object he finds into his mouth. Chewing on such objects often provides relief to the infant. If the objects are not clean, the already inflamed gums provide an excellent opportunity for the harboring of microorganisms and inflammation persists. If relief is not given, the child becomes wakeful, restless and fearful, refuses nourishment, the alimentary canal becomes more active and diarrhea follows. Some times, nausea and vomiting may also ensue.
For most parents, the sudden appearance of the child's first tooth is a momentous occasion. Physicians have also attached great significance to the emergence of primary (milk) tooth/teeth. When the first tooth cuts the gums and starts to erupt, a local inflammatory process occurs which is associated with redness, tenderness, swelling, fever etc. As this process continues, the child puts whatever object he finds into his mouth. Chewing on such objects often provides relief to the infant. If the objects are not clean, the already inflamed gums provide an excellent opportunity for the harboring of microorganisms and inflammation persists. If relief is not given, the child becomes wakeful, restless and fearful, refuses nourishment, the alimentary canal becomes more active and diarrhea follows. Some times, nausea and vomiting may also ensue.
What should you do then?
- Gentle massage of the affected area using a clean finger or a gauze piece lightly soaked in saline should be done.
- Analgesic gels may provide sound relief. Teething rings may be used and they may help the child by providing the child with something to bite on
Issues with teeth in children
Teething
Maintenance of oral hygiene in children
- Tooth brushing
- Flossing
- Mouth rinsing
Dietary measures
- Care during pregnancy
- Care after birth
- Diet management
Decay
- RAMPANT Caries {decay}
- Nursing caries {decay}
Pit and fissure sealing
Habits
Traumatic injuries and their management in children
Space maintainers
Fluorides

Your child's first dental appointment!!!
The first dental appointment for a young child should be planned carefully. Children do not come to the dental clinic on their own; their parents bring them. The child visiting the dental clinic for the very first time could be fearful and apprehensive, this fear and apprehension could be transmitted by parents, friends, family members etc. Before arriving at the operator, the mother should give the child a simple explanation of the visit such as "we are going to see the nice man who wants to see how nicely you brush your teeth". It is also important when speaking to your child, to be careful of how you describe their first visit, not just what you say. For example, if you try to reassure them by telling them it "won't hurt," you are subconsciously telling them that it just might be uncomfortable or painful. If you were planning their first trip for an ice cream, or for a burger or to an amusement park, you would never say, "don't worry it won't hurt." Rather, they can tell from the excitement in your voice and choice of words that it is going to be something fun and exciting, and they will be looking forward to their new experience. Their dental visits can and should be just the same. A generation ago the dental visit for a child began no sooner than when the child was three years old. Today, however a new trend has emerged early visits which should take place when the child is between 6-8 months of age, where parents can bring their children to the dental office and expect some real advice early on as to what to expect in the children's dental development and the prevention of problems later on. The child can accompany the other members of the family in a casual manner to become accustomed to the surroundings and the dental team.
Maintenance of oral hygiene in children
Tooth brushing
 It is recommended that a piece of wet gauze or cloth be used to clean the oral cavity of the child before bedtime. When the first tooth erupts, parents are advised to use the same technique for removal of tooth debris. Also, the parents can use a soft toothbrush without toothpaste till the child has reached the appropriate age, for brushing. After the child has reached this age, a pea-sized amount of fluoridated toothpaste is to be dispensed on the toothbrush and after brushing, rinsing of the oral cavity with water is to be carried out, thereby using the toothpaste itself as a mouth rinse. This should be done under the supervision of parents up to the age of say 7 to 8 years when the child can himself brush his teeth effectively.
It is recommended that a piece of wet gauze or cloth be used to clean the oral cavity of the child before bedtime. When the first tooth erupts, parents are advised to use the same technique for removal of tooth debris. Also, the parents can use a soft toothbrush without toothpaste till the child has reached the appropriate age, for brushing. After the child has reached this age, a pea-sized amount of fluoridated toothpaste is to be dispensed on the toothbrush and after brushing, rinsing of the oral cavity with water is to be carried out, thereby using the toothpaste itself as a mouth rinse. This should be done under the supervision of parents up to the age of say 7 to 8 years when the child can himself brush his teeth effectively.
Flossing
 This is an effective method for removal of debris in between the teeth. Brushing and flossing is considered to be the most effective way of removing debris from all the surfaces of the teeth. Parents for children aged 6-8 years {after which the child can be taught to floss himself and incorporate this in his/her daily maintenance schedule} can do this.
This is an effective method for removal of debris in between the teeth. Brushing and flossing is considered to be the most effective way of removing debris from all the surfaces of the teeth. Parents for children aged 6-8 years {after which the child can be taught to floss himself and incorporate this in his/her daily maintenance schedule} can do this.
Mouth rinsing
The use of anti-microbial agents like sodium fluoride 0.05% f daily are suggested as a valuable adjunct to home care. Young children are not allowed to unsupervised rinsing as they may swallow the entire mouthful, which may have deleterious effects.
Dietary measures
Care during pregnancy
The child gets its calcium, phosphorus and other minerals during the formation of teeth from the mother's blood stream. Hence, a nutritious balanced diet with adequate supplements of minerals, vitamins for expectant mothers must be recommended. Care after birth The lactating mother must take a well balanced diet as mentioned above. Breast-feeding is better than bottle-feeding. It is recommended that feeding in the night be discontinued after the eruption of the first tooth.
Diet management
Infants and children generally need to eat more frequently than 3 times a day. Therefore
- Between meal snacks should consist of foods that have least potential for promoting decay. Sugary snacks and retentive foods should therefore be avoided.
- Potentially harmful foods like cookies, candies, cakes, are better consumed at meal times, than between meals.
- The total amount of sugar consumed is not the key; the frequency of sugar intake and the retentiveness of the food are the important factors.
Decay
1.RAMPANT Caries {decay}
2. Nursing caries {decay}
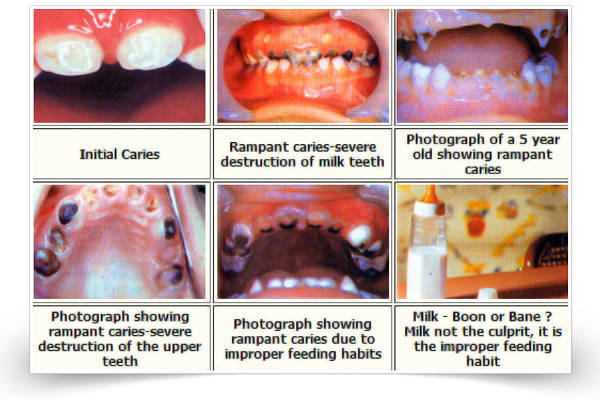
It is the form of decay that affects infants and toddlers. This has been observed in children as young as 12 months of age.
It is associated with:
- Improper use of the nursing bottle, such as putting the infant to bed with the bottle at night or nap time,
- Allowing the child to use the bottle containing sweet solutions like fruit juices.
- Frequent and prolonged, on demand breast feeding once the teeth are erupted.
If there is stagnation of milk or sweetened juices etc. around the teeth for long periods of time, the natural sugar in milk is converted into acid by bacteria and decay begins. This especially occurs in cases of long feeds or feeds during sleep-time. This type of decay spreads quickly and affects a lot of teeth. Weaning should be complete by approximately 18 months of age. Hence, it is advisable to avoid nursing the child to sleep or bottle-feeding the child when it is asleep. At these times water can be used as a pacifier.
Pit and fissure sealing
Advantages
This is basically a non-invasive technique: Sealing of pit and fissure does not allow occurrence of tooth decay..
Fluoride release from fluoridated sealants can confer the protection on the adjoining areas. These sealants usually last for several years and may be dislodged or worn out with certain irregular forces whilst chewing abrasive foods and can be reapplied. Children with newly erupted posterior teeth benefit the most with sealants as these teeth are at the highest risk of developing pit and fissure caries.
Adults also do benefit from the application of sealants
Habits
 "Habit is a tendency towards an act or an act that has become a repeated performance, relatively fixed, consistent, easy to perform and almost automatic."
"Habit is a tendency towards an act or an act that has become a repeated performance, relatively fixed, consistent, easy to perform and almost automatic."
Various habits, which are generally seen in children, are as follows:
Thumb sucking
Tongue thrusting
Mouth breathing
Nail biting
Lip biting etc.
Inadequate knowledge about the source of this problem has been the main reason for unsuccessful termination of these habits. On forceful terminations, the reactions of the child could be rebellion, persistence of the habit, sleep and nourishment problems and learning problems. Over anxious parents tends to force the child to discontinue the habit. This however, does not help. Patience and proper approach are needed to stop this habit.
Thumb-sucking habit is perfectly normal up to the age of 2-3 years. If the habit persists it can cause crowding or irregularities of teeth and even affect the shape of the jaws and the profile. This can be stopped initially by use of local applications to discourage sucking or using a plate for the same at a later stage Habits such as nail biting, tongue thrusting, lip-biting etc. are also bad for the teeth and jaws as they cause undue pressure in certain areas resulting in unwanted movement of teeth or growth of jaws in a particular direction and should be stopped immediately.
Traumatic injuries and their management in children
Accidents are everyday occurrences in the present era. Accidental trauma to the milk teeth mostly occurs during the first three years, because it is during this period that the child is gradually moving from a state of total dependence, with respect to the state of independence as he learns to sit up, crawl, walk and run.
Injuries to teeth, mouth and face of infants and children occur frequently and should not be ignored even in the absence of pain or bleeding. Early observation and treatment of such injuries determines the success of treatment rendered to a great extent An individual can be affected by trauma at any point of life but the incidence of traumatic injuries is most commonly seen in those who indulge in country sports such as football, volleyball, wrestling etc.
Mouth guard is flexible appliance made from plastic and it protects the teeth from trauma. (Children undergoing orthodontic therapy are highly benefited by using mouth guard) Most parents are however, unaware of the utility of the mouth guard and thus do not insist on its wear by their children. Awareness amongst parents will help in reducing the occurrence of injuries to a considerable extent.
Space maintainers
"Space maintenance can be defined as the preservation of the space left by the loss of the primary teeth and sometimes the spaces, which exist naturally." Space maintenance will avoid future crowding and allow the normal eruption of the developing permanent teeth. This is done so that the space required for the new tooth can be kept from being closed by the adjacent teeth. Space maintainer is an appliance, which maintains the width of the lost primary tooth/teeth; thereby restoring function to a certain extent. The space-maintainer can be either removable or fixed.space due to drifting of adjacent teeth to help the proper eruption of the permanent tooth. The space re-gainer can be either removable or fixed.
Fluorides
 Only one method of prevention of decay common to all the countries showing decay reduction is the use of fluoride. Fluorides play a vital role in increasing the resistance of the tooth to decay and also repairing the minor damages due to decay.
Only one method of prevention of decay common to all the countries showing decay reduction is the use of fluoride. Fluorides play a vital role in increasing the resistance of the tooth to decay and also repairing the minor damages due to decay.
The common sources of Fluoride are:
1.Systemic: this includes
Fluoridated water.
Fluoridated salt, milk, flour etc
Fluoride supplements like tablets, drops, lozenges etc.
2.Local: this includes
Tooth paste
Mouth rinse
Professionally, the dentist can apply it in the form of fluoride gels, fluoride solutions and fluoride varnishes. It is best applied on the teeth using a disposable foam lined tray and left in contact with the teeth for 4 minutes.
Different types of regimens are followed to optimize the fluoride uptake and maintain it.
Professional application of fluoride at 6 months intervals is appropriate.

